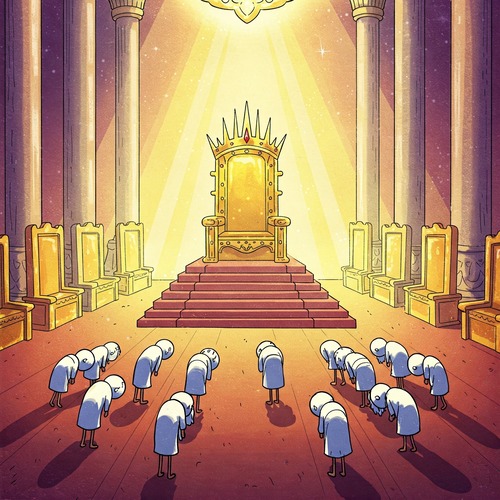
Throne Room: Who Are the 24 Elders Who Cast Their Crowns?
THE MYSTERIOUS HEAVENLY COUNCIL
In Revelation 4, John’s apocalyptic vision transports us into the heavenly throne room. Among the extraordinary sights he witnesses are 24 elders seated on thrones around God’s majestic presence. These mysterious figures, clothed in white garments and wearing golden crowns, perform a striking act of worship: they cast their crowns before God’s throne, declaring, “Worthy are you, our Lord and God, to receive glory and honour and power, for you created all things, and by your will they existed and were created.” (Revelation 4:11)
But who exactly are these 24 elders? Why do they cast down their crowns? And what significance does this heavenly scene hold for believers today? Let’s examine the biblical evidence and Reformed interpretations to uncover the most compelling answer.
THE BIBLICAL DESCRIPTION
Before exploring interpretations, let’s establish what Scripture actually tells us about these figures:
- They sit on thrones surrounding God’s throne They wear white garments
- They wear golden crowns
- They fall down in worship before God
- They cast their crowns before God’s throne
- They possess harps and golden bowls of incense, which are the prayers of the saints (Rev 5:8)
- They sing a new song about redemption (Revelation 5:9-10)
These details have led to several interpretations within Christian theology.
FOUR MAJOR INTERPRETATIONS
Angelic Beings: Some interpreters suggest the elders are angelic beings who serve in God’s heavenly court. They point to similar descriptions of angels elsewhere in Scripture who surround God’s throne in worship.
- Biblical support: Angels are described as wearing white (Mark 16:5) and are often part of God’s heavenly council.
- Challenge: The elders sing about redemption in a way that suggests personal experience (“you ransomed people for God”), which would be unusual for angels.
Glorified Saints: This view holds that the 24 elders represent believers who have died and are now glorified in heaven.
- Biblical support: The white garments and crowns parallel promises made to faithful believers (Rev 2:10, 3:5). Their song about redemption suggests personal experience of salvation.
- Challenge: This scene occurs before the final resurrection and judgement, and raises questions about timing. In other words, if the saints of all time are yet to be raised from their graves, how can they be ‘glorified saints’?
Combined Patriarchs and Apostles: This interpretation sees the elders as representing the 12 patriarchs (tribes of Israel) and the 12 apostles, symbolising the unity of all God’s people—across both testaments.
- Biblical support: The number 24 divides neatly into 12+12. The New Jerusalem in Revelation 21 features both the names of the 12 tribes and the 12 apostles.
- Challenge: There’s no explicit textual connection between the 24 elders and these specific groups.
Symbolic Representatives of All Redeemed People: This view, which has emerged as the majority position among Reformed scholars, sees the elders as symbolic figures representing the entire redeemed church throughout history.
THE CASE FOR THE SYMBOLIC VIEW: THE STRONGEST POSITION
The symbolic interpretation offers the most compelling and biblically consistent understanding for several reasons:
Numbers Matter in Revelation: The number 24 carries significant symbolic weight. In the Old Testament, David organised the priesthood into 24 divisions (1 Chronicles 24:1-19), representing the entire priesthood serving in God’s presence. Similarly, the 24 elders likely represent the entire redeemed community serving as a “kingdom of priests” (Rev 1:6, 5:10).
Their Description Matches Promises to Believers: Everything about the elders corresponds to what Scripture promises believers:
- Thrones: Jesus promised His followers would sit on thrones (Matthew 19:28)
- White robes: Repeatedly promised to faithful believers (Rev 3:5, 6:11, 7:9)
- Golden crowns: Promised as rewards for faithfulness (James 1:12, 1 Peter 5:4)
- Worship posture: The appropriate response of the redeemed (Rev 7:11-12)
They Sing of Redemption: The elders’ song (Revelation 5:9-10) is particularly revealing: it indicates the elders either experienced redemption personally or represent those who did. Their intimate knowledge of salvation points to their connection with humanity rather than being a separate order of heavenly beings.
THE REFORMED CONSENSUS
Notable theologians, GK Beale, William Hendriksen, and Robert Mounce have favoured this representative view. John Calvin, while not definitively settling the question, highlighted the symbolic nature of much of Revelation’s imagery.
WHY DO THEY CAST DOWN THEIR CROWNS?
The crown-casting reveals profound theological truth that aligns perfectly with the Reformed view’s emphasis on God’s sovereignty and glory:
- Recognition of God’s supreme authority: The elders acknowledge that any authority they possess derives entirely from God.
- Rejection of self-glory: By casting down their crowns, they demonstrate that all honour belongs properly to God alone.
- Acknowledgement of grace: Their action visibly demonstrates their rewards are ultimately God’s gifts, not their own achievements, and that salvation is entirely Go’s work, from start to finish.
- Model of true worship: They show that authentic worship involves surrendering all claims to personal merit.
CONCLUSION: THE 24 ELDERS
The 24 elders most convincingly represent the complete assembly of God’s redeemed people, symbolically portrayed in heavenly worship. Their crown-casting demonstrates the perfect response to God’s holiness and grace—a response we’re called to emulate even now.
As we await our own place in that heavenly assembly, may we follow their example, casting whatever “crowns” we possess before the One who alone is worthy of all honour, glory, and praise.
THE 24 ELDERS: RELATED FAQs
Do the 24 elders appear elsewhere in Scripture besides Revelation 4? The 24 elders appear multiple times throughout Revelation, including chapters 4, 5, 7, 11, 14, and 19. Each appearance reinforces their role as worshippers before God’s throne who declare His worthiness and sovereignty. Outside of Revelation, similar concepts appear in Isaiah’s and Ezekiel’s throne room visions, though without the specific number of 24.
- What do contemporary scholars say about the 24 elders? RC Sproul favoured the representative view, suggesting the elders symbolise the church triumphant in glory. Sinclair Ferguson similarly views them as representing the complete covenant community, emphasising their priestly role in offering the prayers of God’s people. Both scholars stress the elders’ worship demonstrates the appropriate response to God’s holiness and grace rather than focusing excessively on their precise identity.
- Is there any archaeological evidence that might illuminate the concept of 24 elders? Ancient Near Eastern royal courts often featured councils of elders who advised kings, which might inform the imagery John uses. Some scholars have noted parallels between the 24 elders and the Sanhedrin or other Jewish ruling councils, suggesting John employed familiar governmental structures to describe heaven’s administration. Archaeological discoveries of ancient throne rooms confirm the surrounding seats for royal advisors was a common arrangement in antiquity.
How do the 24 elders relate to the doctrine of the communion of saints? The 24 elders powerfully visualise the Reformed doctrine of the communion of saints—the spiritual unity of all believers across time and space. Their collective worship demonstrates glorified believers remain active participants in God’s kingdom, not merely passive residents of heaven. Their presentation of the prayers of the saints (Revelation 5:8) suggests a beautiful connection between the church militant on earth and the church triumphant in heaven.
- What significance might the musical instruments of the 24 elders have? The elders’ harps (Revelation 5:8) connect to Temple worship traditions, suggesting continuity between earthly and heavenly praise. These instruments represent the perfection of worship that believers partially experience now but will fully realise in glory. Reformed theologians like John Frame note this heavenly instrumentation validates the use of musical instruments in worship while emphasising that all music should direct attention to God’s glory.
- How have visual depictions of the 24 elders evolved throughout church history? Early Christian art typically portrayed the elders as bearded men wearing white robes and golden crowns, often arranged in semicircles around Christ. Medieval illuminated manuscripts frequently depicted them as a combination of Old Testament patriarchs and New Testament apostles, reinforcing the “12+12” interpretation. Renaissance and modern artistic renderings have increasingly emphasised the diversity of the redeemed, showing elders of various ethnicities to represent believers from “every tribe and language.”
Is there a typological connection between the 24 elders and Old Testament priesthood divisions? Some Reformed scholars, including Vern Poythress and GK Beale, draw direct connections between the 24 elders and the 24 priestly divisions established by David in 1 Chronicles 24. The typological relationship suggests the elders represent a perfected priesthood in heaven, fulfilling the pattern established in Israel’s worship. The priesthood connection strengthens the argument that believers, as a “royal priesthood,” find their ultimate representation in these 24 heavenly figures.
THE 24 ELDERS: OUR RELATED POSTS
Editor's Pick

Will We Remember This Life in Heaven? What Isaiah 65:17 Means
"Will I remember my spouse in heaven? My children? Will the joy we shared on earth matter in eternity?" These [...]

From Empty to Overflow: The Abundant Life Jesus Promised
(AND WHY YOU SHOULDN’T SETTLE FOR LESS) We're surviving, but are we thriving? If we're honest, there's a gap between [...]
What Does Jesus Save Us From?
THREE BIBLE TRUTHS ABOUT SALVATION "Jesus saves." We’ve seen it on bumper stickers, heard it shouted at sporting events, maybe [...]

If God Wants Everyone Saved, Why Aren’t They?
THE REFORMED VIEW ON GOD’S DESIRE VS HIS DECREE The question haunts every believer who has lost an unbelieving loved [...]

The One Man Mystery in Acts 17:26: Is It Adam Or Noah?
When the Apostle Paul stood before the philosophers at Mars Hill, he delivered an insightful statement about human unity: “And [...]
Megiddo Or Jerusalem: Where Did King Josiah Die?
Recent archaeological discoveries at Tel Megiddo continue to reveal evidence of Egyptian military presence during the late 7th century BC, [...]

Losing Your Life Vs Wasting It: How Are the Two Different?
AND WHY DID JESUS PRAISE THE FORMER? Jesus spoke one of the most perplexing statements in Scripture: “For whoever wants [...]

Can Christians Be Demon Possessed? What the Bible Teaches
Perhaps you’ve witnessed disturbing behavior in a professing Christian, or you’ve struggled with persistent sin and wondered if something darker [...]

Sacred Fury: What Christ’s Temple Cleansing Truly Means
Mark 11 records the crack of a handmade whip that echoed through the temple corridors. Tables crashed to the ground, [...]
Did Jesus Cleanse the Temple Twice?
OR DID JOHN DISAGREE WITH THE SYNOPTICS ON TIMING? One of sceptics’ favourite "gotcha" questions targets what they see as [...]
SUPPORT US:
Feel the Holy Spirit's gentle nudge to partner with us?
Donate Online:
Account Name: TRUTHS TO DIE FOR FOUNDATION
Account Number: 10243565459
Bank IFSC: IDFB0043391
Bank Name: IDFC FIRST BANK






